Getting Familiar with MERN - A Modern Web Development Stack

The MERN stack is a popular choice for building modern web applications. This article will introduce you to MERN, explain its components, and show you why it's becoming a go-to solution for developers and companies alike.
💡 Key Takeaways:
Understand what MERN is and its four core components
Learn how the components of MERN work together
Explore real-world examples of MERN stack usage
Basic code examples for each MERN component
What is MERN and Why is it Important?
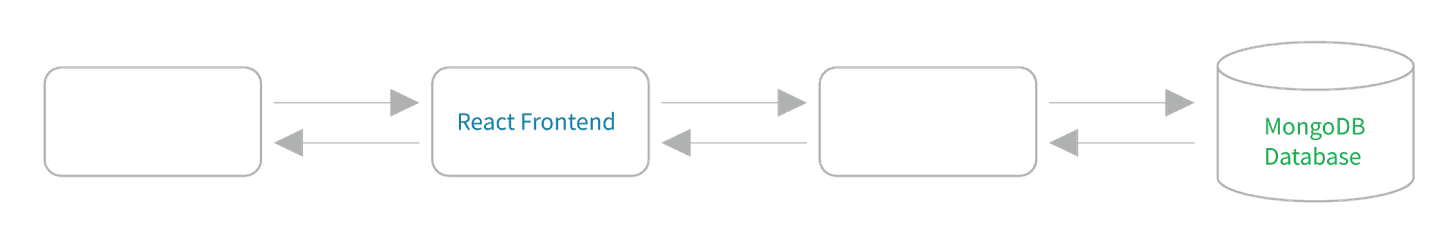
MERN is an acronym that stands for MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js. These four technologies work together to create a full-stack JavaScript environment for building web applications.
MongoDB is a flexible, document-based NoSQL database
Express.js is a minimal and flexible web application framework for Node.js
React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine
The MERN stack allows developers to build entire web applications using only JavaScript. This consistency across the stack can lead to more efficient development and easier maintenance.
How MERN Works
Think of the MERN stack as a relay race team.
React is like the runner who interacts with the audience (users). It's responsible for what the users see and how they interact with the application.
Express.js and Node.js are like the middle-distance runners. They take the baton (data) from React, process it, and pass it along to MongoDB or back to React.
MongoDB is like the anchor of the team. It stores all the important information and passes it back when needed.
In a MERN stack application:
React handles the front-end user interface
Express.js and Node.js manage the back-end server
MongoDB stores the application's data
Here are some code examples for each component.
React
To use React, you'll need Node.js installed. You can create a new React project using Create React App. Here's a simple React component.
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<h1>Welcome to My React Counter!</h1>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>
Click me
</button>
</div>
);
}
export default Counter;
This example shows a simple counter component in React. To try this out, you can create a new React app using Create React App, then replace the content of src/App.js with this code and run the app.
Express.js and Node.js
Express.js runs on Node.js and manages the server-side of your application. Here's a basic Express.js server.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World!');
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
To run this, save it as server.js, run `npm init -y` to create a package.json file, install Express with `npm install express`, and then run `node server.js`.
MongoDB
To use MongoDB, you'll need to sign up for an account. Here's an example of how to connect to MongoDB and perform a basic operation. Make sure to replace '<your_connection_string>' with your actual MongoDB connection string, whether it's a local instance or a cloud-hosted one.
const { MongoClient } = require('mongodb');
async function main() {
const uri = "<your_connection_string>";
const client = new MongoClient(uri);
try {
await client.connect();
console.log("Connected successfully to MongoDB");
const database = client.db("testdb");
const collection = database.collection("devices");
const result = await collection.insertOne({ name: "Smart Phone", brand: "TechCo" });
console.log(`Document inserted with _id: ${result.insertedId}`);
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
} finally {
await client.close();
}
}
main().catch(console.error);
To run this, you'll need to install the MongoDB driver with the`npm install mongodb`, and replace `<username>` and `<password>` with your MongoDB Atlas credentials.
Now that we've explored the components of the MERN stack, let's look at how some well-known companies are using these technologies in production.
Real-World Examples
Many companies leverage the MERN stack or its components.
SEGA partnered with MongoDB to revolutionize its data infrastructure, enabling real-time data analysis and personalized gaming experiences. Read more here.
Walmart and NASA use Node.js to boost performance and scalability in their e-commerce platforms and data processing applications. Read more here.
Netflix utilizes React for its user interface, providing a smooth streaming experience. Read more here.
Airbnb implements React in its front-end development, enabling an interactive and responsive booking system. Read more here.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and scalability of the MERN stack across various industries.
The MERN stack offers a powerful, flexible, and efficient solution for modern web development. Its use of JavaScript throughout the stack, combined with the strengths of each component, makes it an attractive choice for developers and companies alike. From startups to tech giants, companies are leveraging MERN to build scalable, efficient, and user-friendly applications. In our next article, we'll roll up our sleeves and dive into building our own MERN stack application.
💖 Keep experimenting, learning, and honing your skills. Happy coding! 💻
For the full code and detailed screenshots of this project, visit the GitHub repository.